
PCOS and PCOD are medical conditions that affect women’s ovaries. We have frequently heard about PCOS which stands for Polycystic ovary syndrome while PCOD stands for Polycystic ovarian disease. With a slight difference in names, both of them are mistaken to be the same and women do not even know which condition they are suffering from. However, there are some differences that make both medical conditions different.

PCOS
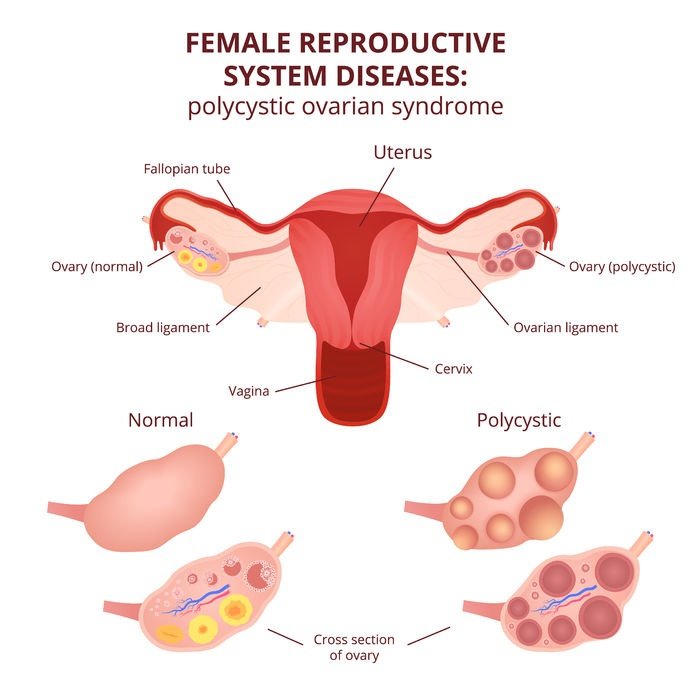
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a medical condition in which women are affected by hormonal imbalances. It is due to the increase of male hormones in the female body, that a woman may experience disturbance in the menstrual cycle and irregular ovulation causes trouble in getting pregnant. Some of the indicators include ovarian cysts, excessive hair growth, and increased male hormones. It is a serious medical condition that requires attention and concern.

PCOD
The polycystic ovarian disease is a condition in which the women’s ovaries produce immature or partially mature eggs in large numbers and over time, cysts are made in the ovaries. Due to this, the size of the ovaries increases and it produces male hormones in large amounts. This causes irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, and also weight gain.

How are they different?
PCOD is a condition in which ovaries produce partially mature eggs and this is likely to happen due to poor lifestyle. On the other hand, PCOS is a severe form of PCOD where ovaries stop releasing eggs. PCOD does not affect fertility greatly as women can ovulate and become pregnant with some help while women who suffer from PCOS may experience difficulty in getting pregnant. Unfortunately, there is a risk of miscarriage or premature birth with PCOS. PCOD and PCOS are usually confused. PCOD is a more common disorder and almost one-third of the women in the world suffer from PCOD while PCOS is a more serious condition and has a relatively less number of patients.
Although, there are slight differences in both and PCOS is more severe than PCOD, both of them can be treated if they are diagnosed in time. A healthy diet and routine can control the symptoms and also improve hormonal imbalances. However, if the symptoms continue to worsen, it is recommended to consult a doctor who can further guide you.




