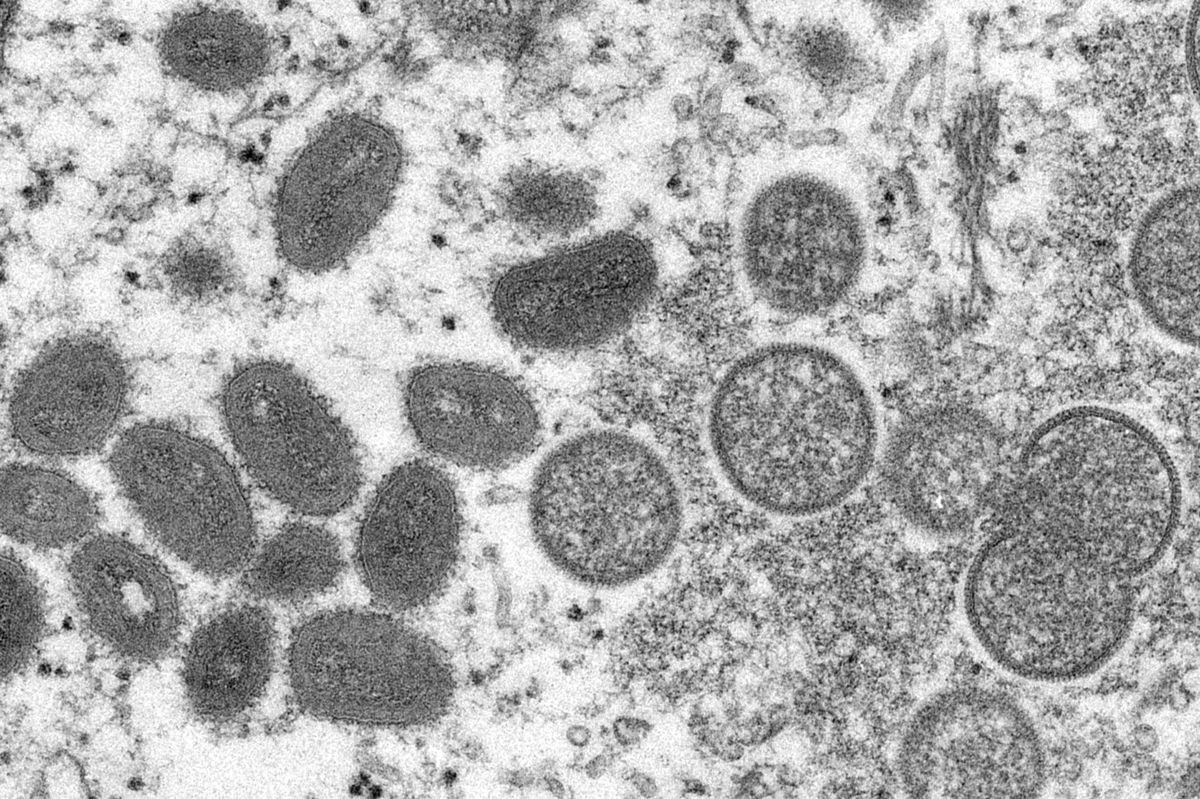
There have been rising cases of a type of viral infection primarily spreading in West and Central Africa. It is commonly known as Monkeypox. Recently, 92 cases of the infection have been confirmed, and 28 more cases are suspected. More cases of similar infection are expected as informed by the United Nations agency. Moreover, there are chances to suspect cases from countries where the disease is not typically found. Here’s all you need to know about the emerging viral infection!

What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a viral infection. It does not spread easily like COVID 19; however, it can be transmitted by coming in close contact with the infected person. Currently, it is also being spread in the genital form which makes it a sexually transmitted disease. This is the reason which has increased the transmission of the virus.
Most of the cases have been reported in the United Kingdom, Spain, and Portugal. Some cases have also been recorded in Canada and Australia. A few public health officials have remarked that cases are more likely to increase in the United States as well.
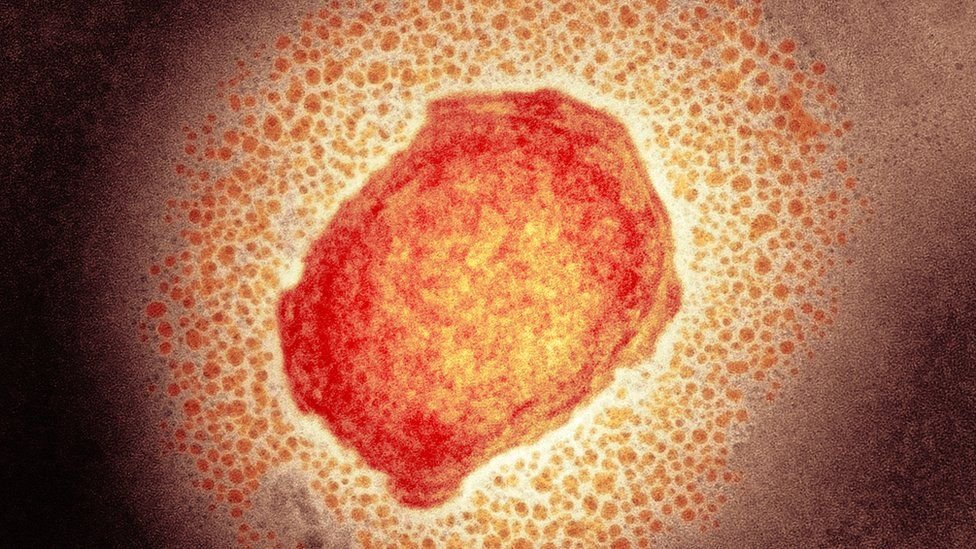
How does Monkeypox spread?
Monkeypox does not spread easily among people. It usually spreads via large respiratory droplets only when people are in close contact with one another. Direct contact can be via bodily fluids however, indirect contact can be via contaminated clothing or bedding.
Common Symptoms
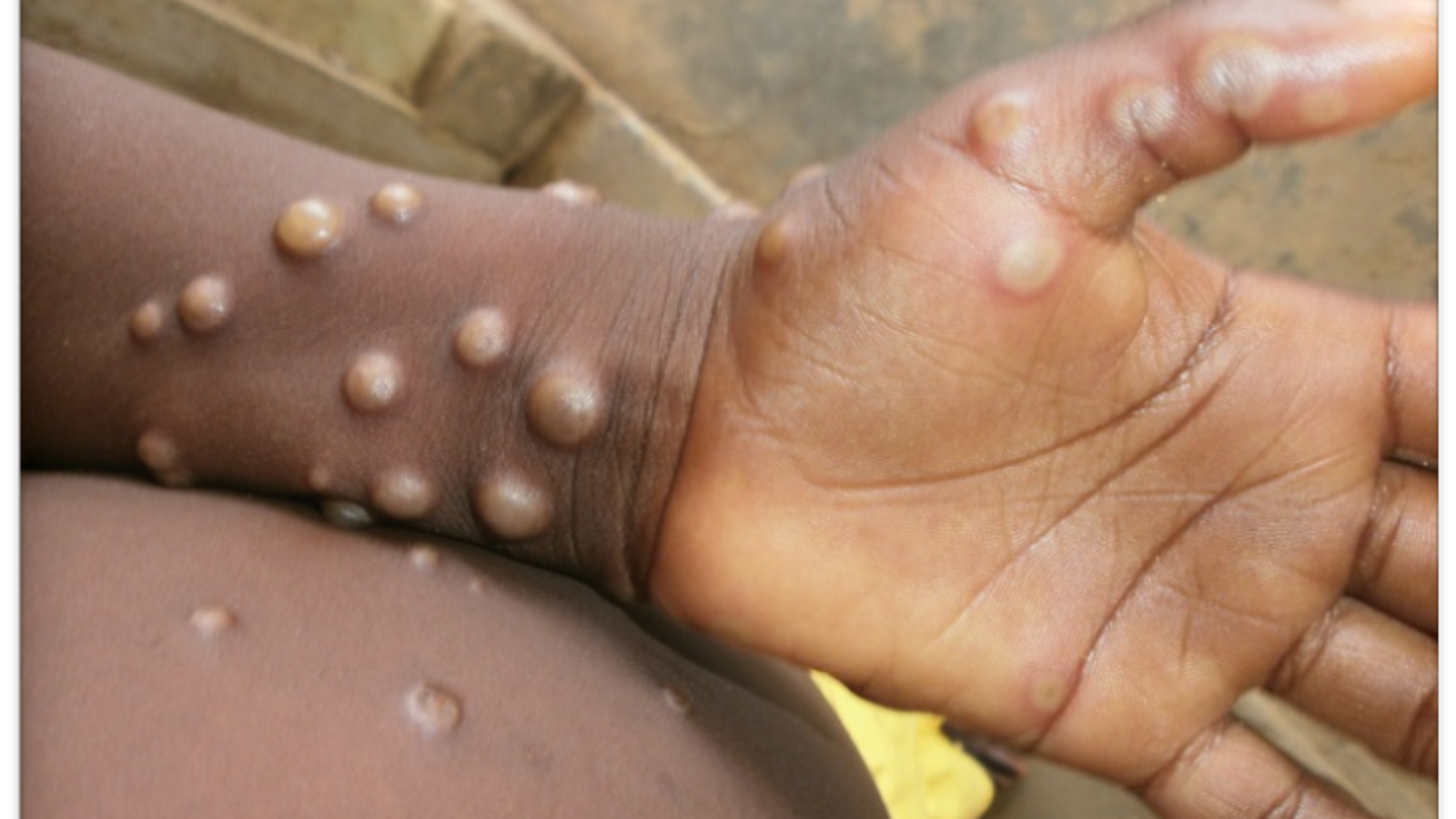
Common symptoms of the virus include fever, body aches, and a distinct bumpy rash. The rash is expected to clear itself within two to four weeks. The rash starts on the face and then spreads to other body parts. The rash boils that fills the pus and then ultimately falls off.
How dangerous is Monkeypox?
In some cases, the viral infection can be deadly. However, those cases are only 1 out of 10%. As directed by a United States official, the risk at the time is low. Most of the people who are infected usually recover in two weeks. The infection may prolong for four weeks after which the infected persons fully recover.



